Error converting content: marked is not a function
icon:: 🛠 tags:: type:: project status:: active sort-key:: 2023.09 start:: Jun 25th, 2024 estimated-end:: end:: next-action:: update purpose and outcome - **Next Action** - TODO update purpose and outcome for P/Berklee AI in Music :LOGBOOK: CLOCK: [2022-06-27 Mon 10:28:07] :END: - **All TODOs on this page** collapsed:: true - {{query (and (task todo) P/Berklee AI in Music )}} - **Important Dates** - Jun 25th, 2024: project init - **Outcome Visioning** - **Purpose & Outcome** - Structured understanding of music production vocabulary, tools and digital landscape - Application of AI - how the know hows' are thinking about it. Take the learning to VoxAI App - **Wins** - Timeline collapsed:: true - Promised Outcome: By the end of the course, you will be able to: collapsed:: true - describe the fundamental concepts of AI and the various types of models used for tasks in music analysis and processing - discuss the technological background behind AI techniques, such as source and vocal separation, melody extraction, and chord recognition, and implement them using available apps and software in the market - grasp the fundamental principles and practical skills required for AI-driven music production, particularly in intelligent mixing and mastering, while exploring the transformative impact of these innovations on music production workflows - identify the key components and AI-based technologies behind song feature extraction, genre classification, recommendation, and personalization systems, recognizing their pivotal role in enhancing music listening experiences - evaluate diverse generative AI neural network architectures used in music composition, including their strengths and weaknesses - describe the different techniques used by GenAI models to assist the composition and songwriting processes - gain practical proficiency in leveraging commercial AI tools and apps to enhance creative music composition processes and workflows - develop a critical mindset for assessing the effectiveness, usefulness, and quality of apps and software used for various applications of AI in music and audio - discuss the complexities and copyright challenges associated with the authorship of GenAI musical works and the training of the deep learning models backing these apps - DAW - are software which combine the functionalities of multitrack recording, MIDI programming, and digital signal processing (DSP), - Week 1: Understanding Musical Content for AI - Introduction to AI foundations and terminology - Fundamentals of machine learning and generative AI - Basics of Python for AI development - **Specialized Python Libraries for AI in Music** collapsed:: true - For AI music applications, Python boasts specialized libraries that handle audio analysis and generation. Libraries, in the context of computer science, are similar to libraries in general; a place where you go for resources and information. In programming, libraries serve as repositories where a wealth of assets including data, documentation, pre-written code, functions, and files are readily available. These collections offer essential resources for efficient coding. - *Librosa* is a library for analyzing audio and music, allowing intricate manipulations of sound data, such as extracting beats or melodies. This is the library we'll be using in this course. - *pyAudio* provides Python bindings for PortAudio, the cross-platform audio I/O library, enabling developers to easily use audio input and output in their Python programs. - *music21* is a tool kit for computer-aided musicology, offering extensive capabilities for analyzing and searching through musical scores. - Other libraries like *Essentia* focus on advanced audio signal processing and music information retrieval tasks. - Musical content representations (sheet music, symbolic, and audio) - **Sheet music representation:** Sheet music, the classical form of music notation, is a visual representation that uses musical symbols to encode the elements of a composition. It includes notes, chords, dynamics, and other musical instructions. This form provides a structured, interpretable format for musicians, encapsulating the melodic, harmonic, and rhythmic aspects of a piece. - Sheet music is primarily represented through Western European music notation - Music theory: This music representation has been developed over centuries, and its nomenclature contains signs and conventions that allow for the formalization of key elements of a musical work, such as structure, tonality, time signature, and form, but also quite precise indications about interpretation and even the intention the composer wishes to imprint on the performance of their work. - 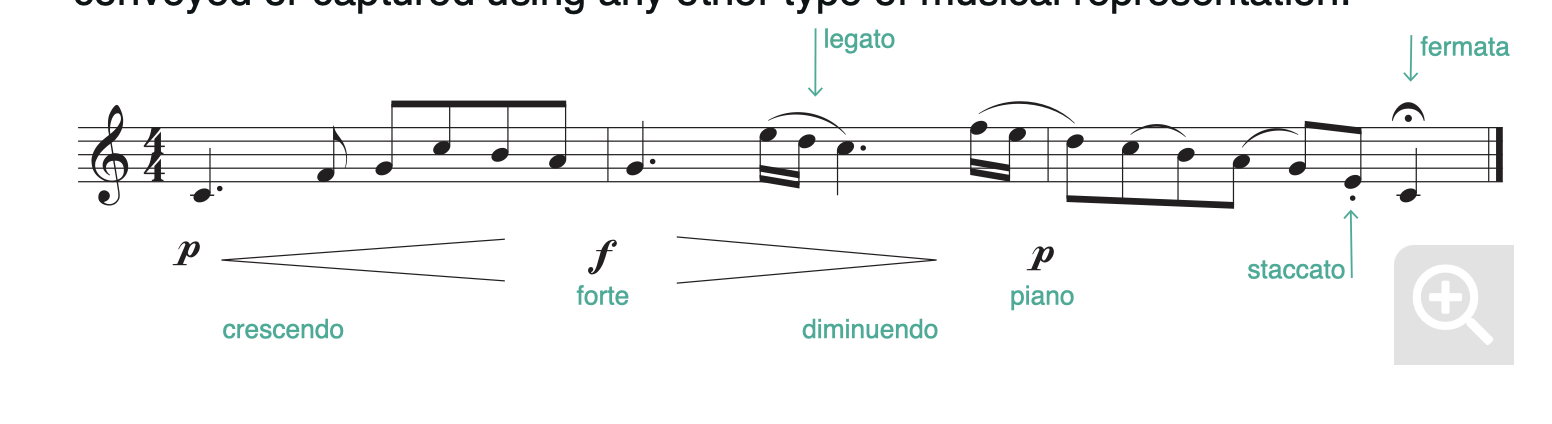 - **Symbolic music representations:** Symbolic music representations, like MIDI, are pivotal in digital music processing. MIDI encodes musical information, including pitch, velocity (which correlates to dynamics), and duration of notes, in a digital format. This form of representation is particularly suited for electronic music production and computational music analysis. - The MIDI (Musical Instrument Digital Interface) standard is an important symbolic representation in the realm of digital music, holding particular significance in the application of machine learning and artificial intelligence to music. - MIDI encodes notes using MIDI note numbers, ranging from 0 to 127, each corresponding to a specific pitc - **Audio representations:** Audio representations like WAV and MP3 capture the actual sound waves of music. This form encodes the acoustic reality of music, including the timbral qualities of instruments and the subtleties of human performance - Spectrograms and Fourier Transform - Assignment: Understanding Musical Content for AI - Week 2: Extracting and Recognizing Musical Elements - Week 3: Music Production and Distribution Using AI - Week 4: Generative AI in Music - Project Summary - Started this project on Jun 25th, 2024 - Interested in getting a Masters degree @ Berklee College of Music - 12 courses phew (12 week each) for $36K collapsed:: true - Requirement - ### Portfolio Applicants to our [Master of Music in Music Production](https://online.berklee.edu/music-degrees/graduate/music-production) degree are required to submit a portfolio. This should include at least three recorded examples of recent work, along with detailed explanations of your specific roles in the works (e.g., DAW used, plug-ins, microphone placements, etc.). Applicants to our [Master of Music in Film Scoring](https://online.berklee.edu/music-degrees/graduate/film-scoring) degree are required to submit a portfolio of two projects, demonstrating your compositional skills scored to picture. It should also include a detailed write-up of your work on the projects, including your concept for the scores and what technologies you used. Applicants to our [Master of Arts in Songwriting](https://online.berklee.edu/music-degrees/graduate/songwriting) degree are required to submit a portfolio. This should include at least two recorded examples of recent work, along with detailed explanations of your specific roles in the works (e.g., co-writer, head writer, responsible for lyrics, verses, chorus, topline writing etc.). Applicants to our [Master of Arts in Interdisciplinary Music Studies](https://online.berklee.edu/music-degrees/graduate/interdisciplinary-music-studies) degree are required to submit a PDF portfolio of at least two recent projects that best showcase your experience and abilities, with a particular focus on the areas of music business, production and technology, and/or composition. The project should touch on your individual artistic practice, interdisciplinary creative vision, technical skills, and awareness of music’s relation to contemporary society. **For all graduate-level degree portfolios, please make sure to include a detailed write-up of the following:** - Your specific role in the project - Your conceptual approach - What technologies you used - If relevant, you can include a paragraph on the collaborative aspects of the project and what challenges you encountered. Students are encouraged to include links to a short video (an unlisted YouTube link or Vimeo link) and/or audio recordings (SoundCloud, Spotify, etc.) to demonstrate the projects discussed. These links can be embedded into the PDF. Please double-check your links to make sure they are accurate and operational, and mark any YouTube videos as unlisted. - TODO Project Wrap Up - TODO Extract and Create Information Packets - TODO Clean up - TODO Write Summary - TODO Add any relevant tags - ### Resources - Sound Resources - [freesound](https://freesound.org/) - [Pixabay (Music category)](https://pixabay.com/music/) - Signals and Systems - MIT course from 2011 - https://ocw.mit.edu/courses/res-6-007-signals-and-systems-spring-2011/, Also a fall course - https://ocw.mit.edu/courses/6-003-signals-and-systems-fall-2011/pages/syllabus/ -